The main aldehyde it has in the wine. It is a distinctive and pleasant element in Jerry’s wines (Spain). However, if a significant amount is present in dining wine, it is considered a deficiency.
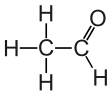
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CHO, sometimes abbreviated by chemists as MeCHO (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale in industry. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants. It is also produced by the partial oxidation of ethanol by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase and is a contributing cause of hangover after alcohol consumption. Pathways of exposure include air, water, land, or groundwater, as well as drink and smoke. Consumption of disulfiram inhibits acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, the enzyme responsible for the metabolism of acetaldehyde, thereby causing it to build up in the body.
|
| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Acetaldehyde | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Ethanal | |||
| Other names
Acetic aldehyde
Ethyl aldehyde Acetylaldehyde | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.761 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H4O | |||
| Molar mass | 44.053 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless gas or liquid | ||
| Odor | Ethereal | ||
| Density | 0.784 g·cm−3 (20 °C) 0.7904–0.7928 g·cm−3 (10 °C) | ||
| Melting point | −123.37 °C (−190.07 °F; 149.78 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 20.2 °C (68.4 °F; 293.3 K) | ||
| miscible | |||
| Solubility | miscible with ethanol, ether, benzene, toluene, xylene, turpentine, acetone slightly soluble in chloroform | ||
| log P | -0.34 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 740 mmHg (20 °C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.57 (25 °C, H2O) | ||
| -.5153−6 cm3/g | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3316 | ||
| Viscosity | 0.21 mPa-s at 20 °C (0.253 mPa-s at 9.5 °C) | ||
| Structure | |||
| trigonal planar (sp2) at C1 tetrahedral (sp3) at C2 | |||
| 2.7 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
89 J·mol−1·K−1 | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
160.2 J·mol−1·K−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−192.2 kJ·mol−1 | ||
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
-127.6 kJ·mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
potential occupational carcinogen | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   | |||
| H224, H319, H335, H351 | |||
| P210, P261, P281, P305+P351+P338 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −39.00 °C; −38.20 °F; 234.15 K | ||
| 175.00 °C; 347.00 °F; 448.15 K | |||
| Explosive limits | 4.0–60% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
1930 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
13,000 ppm (rat), 17,000 ppm (hamster), 20,000 ppm (rat) | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
200 ppm (360 mg/m3) | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
2000 ppm | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | HMDB | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related aldehydes
|
Formaldehyde Propionaldehyde | ||
Related compounds
|
Ethylene oxide | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Acetaldehyde (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has listed acetaldehyde as a Group 1 carcinogen. Acetaldehyde is "one of the most frequently found air toxins with cancer risk greater than one in a million".

 Wineries
Wineries